Generate Secondary Access Key For Blob In Azure
- Generate Secondary Access Key For Blob In Azure Free
- Azure Blob Storage Account Key
- Generate Secondary Access Key For Blob In Azure Windows
- Azure Blob Storage Access Control
[AZURE.INCLUDE storage-selector-portal-create-storage-account]
Overview
Az storage account keys list List the access keys or Kerberos keys (if active directory enabled) for a storage account. Az storage account keys renew Regenerate one of the access keys or Kerberos keys (if active directory enabled) for a storage account. Name or ID of subscription. You can configure. May 13, 2016 When you create a storage account, Azure generates two 512-bit storage access keys, which are used for authentication when the storage account is accessed. By providing two storage access keys, Azure enables you to regenerate the keys with no interruption to your storage service or access to that service.
An Azure storage account provides a unique namespace to store and access your Azure Storage data objects. All objects in a storage account are billed together as a group. By default, the data in your account is available only to you, the account owner.
[AZURE.INCLUDE storage-account-types-include]
Storage account billing
[AZURE.INCLUDE storage-account-billing-include]
[AZURE.NOTE] When you create an Azure virtual machine, a storage account is created for you automatically in the deployment location if you do not already have a storage account in that location. So it's not necessary to follow the steps below to create a storage account for your virtual machine disks. The storage account name will be based on the virtual machine name. See the Azure Virtual Machines documentation for more details.
Generate Secondary Access Key For Blob In Azure Free
Storage account endpoints
Every object that you store in Azure Storage has a unique URL address. The storage account name forms the subdomain of that address. The combination of subdomain and domain name, which is specific to each service, forms an endpoint for your storage account.
For example, if your storage account is named mystorageaccount, then the default endpoints for your storage account are:
Blob service: http://mystorageaccount.blob.core.windows.net
Table service: http://mystorageaccount.table.core.windows.net
Queue service: http://mystorageaccount.queue.core.windows.net
File service: http://mystorageaccount.file.core.windows.net
[AZURE.NOTE] A Blob storage account only exposes the Blob service endpoint.
The URL for accessing an object in a storage account is built by appending the object's location in the storage account to the endpoint. For example, a blob address might have this format: http://mystorageaccount.blob.core.windows.net/mycontainer/myblob.
You can also configure a custom domain name to use with your storage account. For classic storage accounts, see Configure a custom domain Name for your Blob Storage Endpoint for details. For Resource Manager storage accounts, this capability has not been added to the Azure portal yet, but you can configure it with PowerShell. For more information, see the Set-AzureRmStorageAccount cmdlet.
Create a storage account
Sign in to the Azure portal.
On the Hub menu, select New -> Data + Storage -> Storage account.
Enter a name for your storage account. See Storage account endpoints for details about how the storage account name will be used to address your objects in Azure Storage.
[AZURE.NOTE] Storage account names must be between 3 and 24 characters in length and may contain numbers and lowercase letters only.
Your storage account name must be unique within Azure. The Azure portal will indicate if the storage account name you select is already in use.
Specify the deployment model to be used: Resource Manager or Classic. Resource Manager is the recommended deployment model. For more information, see Understanding Resource Manager deployment and classic deployment.
[AZURE.NOTE] Blob storage accounts can only be created using the Resource Manager deployment model.
Select the type of storage account: General purpose or Blob storage. General purposeGenerating key words to find scholarly sources. is the default.
If General purpose was selected, then specify the performance tier: Standard or Premium. The default is Standard. For more details on standard and premium storage accounts, see Introduction to Microsoft Azure Storage and Premium Storage: High-Performance Storage for Azure Virtual Machine Workloads.
If Blob Storage was selected, then specify the access tier: Hot or Cool. The default is Hot. See Azure Blob Storage: Cool and Hot tiers for more details.
Select the replication option for the storage account: LRS, GRS, RA-GRS, or ZRS. The default is RA-GRS. For more details on Azure Storage replication options, see Azure Storage replication.
Select the subscription in which you want to create the new storage account.
Specify a new resource group or select an existing resource group. For more information on resource groups, see Azure Resource Manager overview.
Select the geographic location for your storage account. See Azure Regions for more information about what services are available in which region.
Click Create to create the storage account.
Manage your storage account
Change your account configuration
After you create your storage account, you can modify its configuration, such as changing the replication option used for the account or changing the access tier for a Blob storage account. In the Azure portal, navigate to your storage account, click All settings and then click Configuration to view and/or change the account configuration.
[AZURE.NOTE] Depending on the performance tier you chose when creating the storage account, some replication options may not be available.
Changing the replication option will change your pricing. For more details, see Azure Storage Pricing page.
For Blob storage accounts, changing the access tier may incur charges for the change in addition to changing your pricing. Please see the Blob storage accounts - Pricing and Billing for more details.
Manage your storage access keys
When you create a storage account, Azure generates two 512-bit storage access keys, which are used for authentication when the storage account is accessed. By providing two storage access keys, Azure enables you to regenerate the keys with no interruption to your storage service or access to that service.
[AZURE.NOTE] We recommend that you avoid sharing your storage access keys with anyone else. To permit access to storage resources without giving out your access keys, you can use a shared access signature. A shared access signature provides access to a resource in your account for an interval that you define and with the permissions that you specify. See Shared Access Signatures: Understanding the SAS model for more information.
View and copy storage access keys
In the Azure portal, navigate to your storage account, click All settings and then click Access keys to view, copy, and regenerate your account access keys. The Access Keys blade also includes pre-configured connection strings using your primary and secondary keys that you can copy to use in your applications.
Regenerate storage access keys
We recommend that you change the access keys to your storage account periodically to help keep your storage connections secure. Two access keys are assigned so that you can maintain connections to the storage account by using one access key while you regenerate the other access key.
[AZURE.WARNING] Regenerating your access keys can affect services in Azure as well as your own applications that are dependent on the storage account. All clients that use the access key to access the storage account must be updated to use the new key.
Media services - If you have media services that are dependent on your storage account, you must re-sync the access keys with your media service after you regenerate the keys.
Applications - If you have web applications or cloud services that use the storage account, you will lose the connections if you regenerate keys, unless you roll your keys.
Storage Explorers - If you are using any storage explorer applications, you will probably need to update the storage key used by those applications. Cyberlink powerdvd 7 cd key generator.
Here is the process for rotating your storage access keys:
Update the connection strings in your application code to reference the secondary access key of the storage account.
Regenerate the primary access key for your storage account. On the Access Keys blade, click Regenerate Key1, and then click Yes to confirm that you want to generate a new key.
Update the connection strings in your code to reference the new primary access key.
Regenerate the secondary access key in the same manner.
Delete a storage account
To remove a storage account that you are no longer using, navigate to the storage account in the Azure portal, and click Delete. Deleting a storage account deletes the entire account, including all data in the account.
[AZURE.WARNING] It's not possible to restore a deleted storage account or retrieve any of the content that it contained before deletion. Be sure to back up anything you want to save before you delete the account. This also holds true for any resources in the account—once you delete a blob, table, queue, or file, it is permanently deleted.
To delete a storage account that is associated with an Azure virtual machine, you must first ensure that any virtual machine disks have been deleted. If you do not first delete your virtual machine disks, then when you attempt to delete your storage account, you will see an error message similar to:
If the storage account uses the Classic deployment model, you can remove the virtual machine disk by following these steps in the Azure portal:
Azure Blob Storage Account Key
- Navigate to the classic Azure portal.
- Navigate to the Virtual Machines tab.
- Click the Disks tab.
- Select your data disk, then click Delete Disk.
- To delete disk images, navigate to the Images tab and delete any images that are stored in the account.
For more information, see the Azure Virtual Machine documentation.
Next steps
- Visit the Azure Storage Team Blog.
| title | titleSuffix | description | services | author | ms.service | ms.topic | ms.date | ms.author |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Azure Storage | Learn how to view, manage, and rotate your storage account access keys. | tamram | how-to | tamram |
When you create a storage account, Azure generates two 512-bit storage account access keys. These keys can be used to authorize access to data in your storage account via Shared Key authorization.
Generate Secondary Access Key For Blob In Azure Windows

Azure Blob Storage Access Control
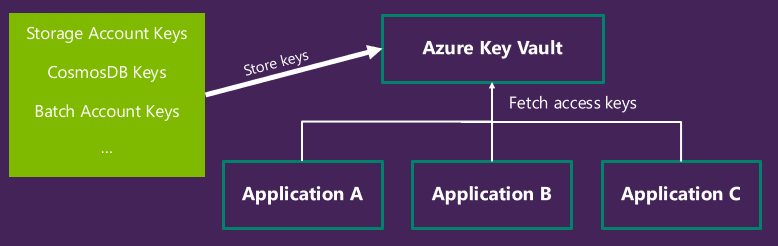
Microsoft recommends that you use Azure Key Vault to manage your access keys, and that you regularly rotate and regenerate your keys. Using Azure Key Vault makes it easy to rotate your keys without interruption to your applications. You can also manually rotate your keys.
[!INCLUDE storage-account-key-note-include]
View access keys and connection string
[!INCLUDE storage-view-keys-include]
Use Azure Key Vault to manage your access keys
Microsoft recommends using Azure Key Vault to manage and rotate your access keys. Your application can securely access your keys in Key Vault, so that you can avoid storing them with your application code. For more information about using Key Vault for key management, see the following articles:
Manually rotate access keys
Microsoft recommends that you rotate your access keys periodically to help keep your storage account secure. If possible, use Azure Key Vault to manage your access keys. If you are not using Key Vault, you will need to rotate your keys manually.
Two access keys are assigned so that you can rotate your keys. Having two keys ensures that your application maintains access to Azure Storage throughout the process.
[!WARNING]Regenerating your access keys can affect any applications or Azure services that are dependent on the storage account key. Any clients that use the account key to access the storage account must be updated to use the new key, including media services, cloud, desktop and mobile applications, and graphical user interface applications for Azure Storage, such as Azure Storage Explorer.
Follow this process to rotate your storage account keys:
- Update the connection strings in your application code to use the secondary key.
- Regenerate the primary access key for your storage account. On the Access Keys blade in the Azure portal, click Regenerate Key1, and then click Yes to confirm that you want to generate a new key.
- Update the connection strings in your code to reference the new primary access key.
- Regenerate the secondary access key in the same manner.
[!NOTE]Microsoft recommends using only one of the keys in all of your applications at the same time. If you use Key 1 in some places and Key 2 in others, you will not be able to rotate your keys without some application losing access.
To rotate an account's access keys, the user must either be a Service Administrator, or must be assigned an RBAC role that includes the Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/regeneratekey/action. Some built-in RBAC roles that include this action are the Owner, Contributor, and Storage Account Key Operator Service Role roles. For more information about the Service Administrator role, see Classic subscription administrator roles, Azure RBAC roles, and Azure AD roles. For detailed information about built-in RBAC roles for Azure Storage, see the Storage section in Azure built-in roles for Azure RBAC.



