Openssl Rsa Generate Key Example
4).Encryption and Decryption Example code. 1).Generate RSA keys with OpenSSL. Use the below command to generate RSA keys with length of 2048. Openssl genrsa -out private.pem 2048. Extract public key from private.pem with the following command. Openssl rsa -in private.pem -outform PEM -pubout -out public.pem. Public.pem is RSA public key in PEM.
Introduction
- RSAgeneratekeyex generates a 2-prime RSA key pair and stores it in the RSA structure provided in rsa. The pseudo-random number generator must be seeded prior to calling RSAgeneratekeyex. The pseudo-random number generator must be seeded prior to calling RSAgeneratekeyex.
- I'm trying to create a private key and having an issue. When I use ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C 'youremail@example.com', I get a private key in the following format. As workaround I've used older version of openssh to generate key. You can test if your generated key is correct with openssl rsa -text -in keyfile -passin 'pass:passphrase'.
- RSAgeneratekeyex generates a 2-prime RSA key pair and stores it in the RSA structure provided in rsa. The pseudo-random number generator must be seeded prior to calling RSAgeneratekeyex. The pseudo-random number generator must be seeded prior to calling RSAgeneratekeyex.
- I'm adding https support to an embedded linux device. I have tried to generate a self-signed certificate with these steps: openssl req -new cert.csr openssl rsa -in privkey.pem -out key.pem openssl x509 -in cert.csr -out cert.pem -req -signkey key.pem -days 1001 cat key.pemcert.pem.
A Certificate Signing Request (CSR) is the first step in setting up an SSL Certificate on your website. SSL certificates are provided by Certificate Authorities (CA), which require a Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
This guide will instruct you on how to generate a Certificate Signing Request using OpenSSL.
- Access to a user account with root or sudo privileges
- A command line/terminal window
- If you’re working on a remote server, an established SSH connection to the server
- OpenSSL needs to be installed on your system to generate the key
- A text editor, such as nano, to view your key
Open a terminal window. Use your SSH connection to log into your remote server.
Note: If you are working locally, you don’t need an SSH connection. Also, most Linux systems will launch a terminal window by pressing Ctrl-Alt-T or Ctrl-Alt-F1.
Step 2: Create an RSA Private Key and CSR
It is advised to issue a new private key each time you generate a CSR. Hence, the steps below instruct on how to generate both the private key and the CSR.
Make sure to replace your_domain with the actual domain you’re generating a CSR for.
The commands are broken out as follows:
- openssl – activates the OpenSSL software
- req – indicates that we want a CSR
- –new –newkey – generate a new key
- rsa:2048 – generate a 2048-bit RSA mathematical key
- –nodes – no DES, meaning do not encrypt the private key in a PKCS#12 file
- –keyout – indicates the domain you’re generating a key for
- –out – specifies the name of the file your CSR will be saved as
Note: Use 2048-bit key pairs. The 4096-bit key pairs are more secure, however, they require a lot more server resources.
Your system should launch a text-based questionnaire for you to fill out.
Enter your information in the fields as follows:
- Country Name – use a 2-letter country code (US for the United States)
- State – the state in which the domain owner is incorporated
- Locality – the city in which the domain owner is incorporated
- Organization name – the legal entity that owns the domain
- Organizational unit name – the name of the department or group in your organization that deals with certificates
- Common name – typically the fully qualified domain name (FQDN), i.e. what the users type in a web browser to navigate to your website
- Email address – the webmaster’s email address
- Challenge password – an optional password for your key pair
Please take into account that Organization Name and Unit Name must not contain the following characters:
< > ~ ! @ # $ % ^ * / ( ) ?.,&
Once the software finishes, you should be able to find the CSR file in your working directory.
You can also enter the following:
The system should list out all certificate signing requests on the system. The one that matches the domain name you provided in Step 2 appended with the .csr extension is the one you need to look into.
Step 5: Submit the CSR as Part of Your SSL Request
You can open the .csr file in a text editor to find the alphanumeric code that was generated.
Enter the following command:
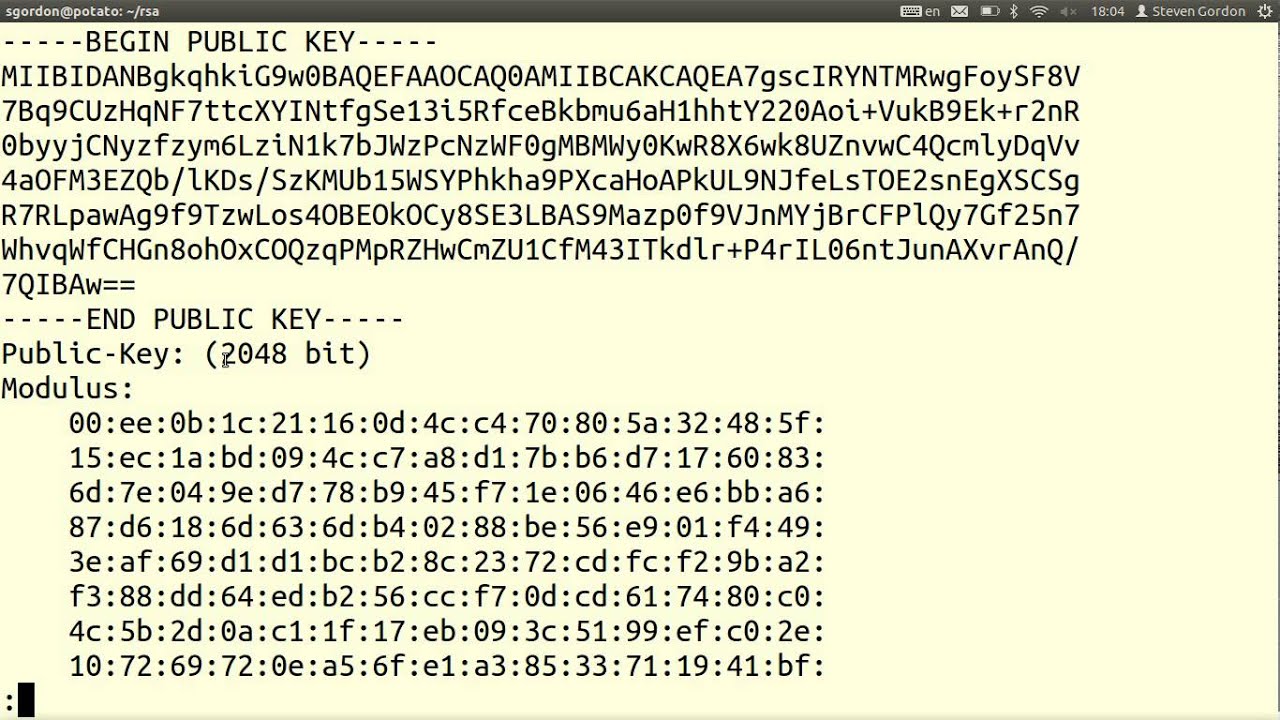
This text can be copied and pasted into a submittal form to request your SSL certificate from a Certificate Authority.
Make sure you copy the entire text. Some CAs may allow you to simply upload the .csr file you generated. Below is an example of a CSR.
You needn’t send the private key to the CA. Once you get your SSL certificate, the private key on the server will bind with it to encrypt communication.
Now you know how to generate an OpenSSL certificate signing request. Before submitting the CSR to a certificate authority, we recommend verifying the information it holds. Use one of the widely available online CSR decoders.
SSL is a crucial protocol for securing traffic between a website and its visitors. It helps to protect sensitive information online, such as credit card data.
Next, You Should Also Read:
Generate private key for an SSL certificate and verify its consistency.
Generate unencrypted private key
Rsa_generate_key Openssl
Generate 4096-bit private key using RSA algorithm.
Generate encrypted private key
Basic way to generate encrypted private key
Generate 4096-bit RSA private key, encrypt it using AES-192 cipher and password provided from the application itself as you will be asked for it.
Different ways to generate encrypted private key
Generate 4096-bit RSA private key, encrypt it using 3DES cipher and password provided from the command-line.
Generate 4096-bit RSA private key, encrypt it using AES-128 cipher and password provided from the specific file.
Generate 4096-bit RSA private key, encrypt it using CAMELLIA-256 cipher and password provided from the environment variable.
Generate 4096-bit RSA private key, encrypt it using AES-256 cipher and password provided from standard input.
Encrypt or decrypt existing private key
Encrypt existing private key using AES-256 cipher and password provided from the command-line.
Re-encrypt existing private key using AES-256 cipher and password provided from the command-line.
Decrypt existing private key using password provided from the command-line.
Verify consistency of the private key
Verify consistency of the private key using password provided from the command-line.

Result when private key's integrity is not compromised.
Result when private key's integrity is compromised.
Additional information
Openssl Generate Key File
You can still use the following command to generate private key.
Openssl Rsa Generate Key Example Excel
This way is still supported, so existing shell scripts will work without any changes.



